 የጥበቃ እና መዝናኛ መምሪያ
የጥበቃ እና መዝናኛ መምሪያ መጠበቅ. መከላከል. መደሰት.
 የጥበቃ እና መዝናኛ መምሪያ
የጥበቃ እና መዝናኛ መምሪያ  ማውጫ
ማውጫየባህር ረግረጋማዎች
ይህ ቡድን ሁሉንም በየወቅቱ በጎርፍ የሚጥለቀለቁ የእንጨት እፅዋትን፣ እንዲሁም የተሟሉ ደኖችን፣ የተጠለሉ እና በውቅያኖስ አቅራቢያ ያሉ የባህር እርጥብ መሬቶችን ያጠቃልላል። በባሕር ዳርቻዎች ውስጥ የአንድ ተክል ዓይነት የዕፅዋት ፊዚዮጂዮሚ በከፍተኛ ደረጃ ተለዋዋጭ ሊሆን ይችላል እንደ ተከታታይ የእድገት ደረጃ እና በንፋስ እና በጨው ርጭት ለመግረዝ የተጋለጠ ነው. በውጤቱም, ተመሳሳይ የእጽዋት አይነት በተለያዩ ሁኔታዎች ውስጥ በተለያዩ ቦታዎች ላይ እንደ ቁጥቋጦ, ጫካ ወይም ጫካ ሊገለጽ ይችላል. ጥሩ ምሳሌ ጥቁር ዊሎው (ሳሊክስ ኒግራ) የባህር ረግረጋማ ደን ሲሆን መጀመሪያ ላይ እንደ ቁጥቋጦ መሬት ሊመሰረት ይችላል ነገር ግን ዛፎቹ ሲበስሉ በፍጥነት የጫካ መሬት ወይም የደን ቁመት ይደርሳል። ቢሆንም, ይህ ቡድን በአጠቃላይ የባሕር ቁጥቋጦ ረግረጋማ እና የባሕር ረግረጋማ ደኖች, ያላቸውን ብስለት physiognomy, ነገር ግን ደግሞ floristic ጥንቅር ብቻ ሳይሆን, ሊከፋፈል ይችላል.
የባህር ቁጥቋጦዎች ረግረጋማ ቦታዎች በየወቅቱ በጎርፍ ተጥለቅልቀዋል፣ ብዙውን ጊዜ ጥቅጥቅ ያሉ ቁጥቋጦዎች የተጠለሉ ፣ ከኋላ ያሉ ጉድጓዶች እና የመግቢያ ጭንቅላቶች ፣ የገጽታ ውሃ በዓመቱ ውስጥ ይገኛል። የተደረደሩ የውሃ ጠረጴዛዎች እና ከወቅታዊ የጎርፍ መጥለቅለቅ ጋር የሃይድሮሎጂ ባህሪን ያሳያሉ። ሁለቱም የከርሰ ምድር ውሃ እና የገጽታ ውሀዎች ትኩስ ናቸው (< 0.5 ppt) ምንም እንኳን የጨው ውሃ በእነዚህ ቦታዎች ላይ ሊዋሃድ ቢችልም እንደ አውሎ ንፋስ ባሉ ክስተቶች ወቅት ከፍተኛ የሆነ አውሎ ንፋስ ከተከሰተ በኋላ። አፈር የተዘረጋ ነው፣ እርጥብ አሸዋ ላይ እስከ 30 ሴሜ (12 ኢንች) የሚደርስ ስስ ሽፋን ያለው ሙክ። የእነዚህ ማህበረሰቦች ዝርያዎች በጣም ተለዋዋጭ ናቸው እና ከደቡብ ምስራቅ የባህር ዳርቻ (የቨርጂኒያ የባህር ዳርቻ ከተማ) ወደ ምስራቃዊ የባህር ዳርቻ (አኮማክ እና ኖርዝአምፕተን ካውንቲ) በመጠኑ ይቀየራል። በመላው ክልል፣ ሰም ማይርትል (Morella cerifera) የባህሪው የበላይ ነው። ደቡባዊ አካባቢዎች ኢንክቤሪ (ኢሌክስ ግላብራ) እና ከፍተኛ ቡሽ ብሉቤሪ (Vccinium spp.) ይይዛሉ። በምስራቅ የባህር ዳርቻ በሰሜን በኩል በዚህ ቡድን ውስጥ እነዚህ ዝርያዎች እምብዛም አስፈላጊ አይደሉም. የመርዝ አረግ ወይን መውጣት (Toxicodendron radicans var. radicans) በአብዛኛው በእነዚህ ረግረጋማ ቦታዎች ከቁጥቋጦዎች ጋር በብዛት የተሳሰሩ ናቸው። የእጽዋት ሽፋኖች ንጉሣዊ ፈርን ጨምሮ በፈርን የበለፀጉ ሊሆኑ ይችላሉ (Osmunda spectabilis), ማርሽ ፈርን (Thelypteris palustris var. pubescens), የተጣራ ሰንሰለት ፈርን (Lorinseria areolata) እና ቨርጂኒያ ሰንሰለት ፈርን (ዉድዋርዲያ ቪርጂኒካ), ነገር ግን እንደ whorled Marsh-pennywort (Hydrocotyle verticillata) ያሉ የተለያዩ forbs ያካትታሉ. የባህር ቁጥቋጦ ረግረጋማ ምደባ፣ ጂኦግራፊያዊ ስርጭት እና ጥበቃ ሁኔታ በአሁኑ ጊዜ በተወሰነ ደረጃ እርግጠኛ ያልሆኑ እና ጥልቅ ጥናት ያስፈልጋቸዋል።
Maritime swamp forests are seasonally flooded and saturated forests occupying large, protected, interdune swales, flats immediately behind tidal marshes, and the bottoms of streams just inland from estuarine zones. These communities definitely occur from southern New Jersey to North Carolina, but may range further south. In Virginia, stands are scattered along the outer Coastal Plain from the Eastern Shore (Accomack and Northampton Counties) to Cape Henry and False Cape (City of Virginia Beach). The status of these communities on the western shore of the Chesapeake Bay is less clear. Habitats are generally characterized by hummock-and-hollow microtopography, with mucky to sandy, mottled soils and sizeable areas of seasonally standing water. The apparent nutrient status and flooding regimes of soils are highly variable and probably relate to the wide compositional variation in documented stands. Dominant overstory trees in the seasonally flooded forests of the group include red maple (Acer rubrum), sweetgum (Liquidambar styraciflua), swamp tupelo (Nyssa biflora), blackgum (Nyssa sylvatica), black willow (Salix nigra), sweetbay magnolia (Magnolia virginiana var. virginiana) and, less frequently, bald cypress (Taxodium distichum) and Atlantic white-cedar (Chamaecyparis thyoides). Shrubs are diverse but usually include highbush blueberries (Vaccinium fuscatum and/or Vaccinium formosum), wax myrtle (Morella cerifera), red bay (Persea palustris), and greenbriers (Smilax spp.). Herb layers range from floristically depauperate, with dominance by Virginia chain fern (Woodwardia virginica) or low shrubs, to species-rich with a diversity of marsh and swamp species.
Saturated pine forests in this group occur in back-dune depressions of barrier islands and on terrace flats bordering estuaries further inland. In Virginia, these communities are locally scattered along the Chesapeake Bay (both shores) and its major estuarine tributaries, as well as around Back Bay and estuarine tributaries of Currituck Sound in the southeastern corner of the state. Occasionally, stands occupy slightly elevated "islands" within the upper portions of salt marshes. Habitats are level flats with shallow water tables and hummock-and-hollow microtopography. Areas of seasonally ponded water and organic muck are present; elsewhere, soils are heavily mottled sands. Loblolly pine (Pinus taeda) is the usual dominant overstory tree, sometimes with hardwood associates. Wax myrtle (Morella cerifera) and vines of common greenbrier (Smilax rotundifolia) and poison ivy (Toxicodendron radicans var. radicans) are usually abundant. In southern areas (e.g., on False Cape), pond pine (Pinus serotina) and inkberry (Ilex glabra) are characteristic woody associates. Wetland species such as cinnamon fern (Osmundastrum cinnamomeum), royal fern (Osmunda spectabilis), switchgrass (Panicum virgatum var. virgatum and var. cubense), and smartweeds (Persicaria spp.) dominate species-poor herb layers. A distinctive variant occurring in southeastern Virginia and North Carolina has a dense understory of switch cane (Arundinaria tecta). Some of the maritime wet pine forests appear to represent formerly open, bog-like maritime grasslands that have been invaded by loblolly pines. There is a well documented example of this variant from the Eastern Shore (Assateague Island, Accomack County) and at least one poorly documented occurrence on False Cape (City of Virginia Beach). These stands occupy swales in sheltered back dunes that are protected from salt spray except during major storm surges. A thin organic layer, frequently covered by dense mats of Sphagnum mosses, is usually present at the soil surface. On Assateague Island the vegetation is an open stand of young, salt-spray-stunted loblolly pine, with a very sparse shrub layer. Cranberry (Vaccinium macrocarpon) forms dense mats locally beneath the pines. Elsewhere, scattered herbs include saltmeadow cordgrass (Spartina patens), tall flat panic grass (Coleataenia rigidula ssp. rigidula), and switchgrass (Panicum virgatum var. virgatum) in shallow pools and depressions, and bushy bluestem (Andropogon glomeratus), Virginia marsh St. John's-wort (Triadenum virginicum), beaksedges (Rhynchospora spp.), twisted yellow-eyed grass (Xyris torta), white-bracted thoroughwort (Eupatorium leucolepis), and water sundew (Drosera intermedia) in wet sand and Sphagnum mats. Maritime Wet Pine Forests are similar to and often intergrade with non-wetland maritime loblolly pine forests and maritime evergreen forests.
የባህር ረግረጋማ ሥነ-ምህዳራዊ ተለዋዋጭነት እና ከውስጥ ከሚገኙ ረግረጋማ ደኖች የሚለዩት በደንብ አልተረዳም። እንደሌሎች የባህር ዞን ማህበረሰቦች በአውሎ ንፋስ ፣በጨው ርጭት እና በዱር መዘዋወር ምክንያት ረብሻ ይደርስባቸዋል። የባህር ላይ ረግረጋማ ደኖች በቨርጂኒያ ውስጥ ብርቅዬ አይደሉም እና ልማትን ፣ ቁጥቋጦን እና የግብርና ብክለትን ሊጎዱ ይችላሉ።
ማጣቀሻዎች፡- ሃርቪል (1967)፣ ፍሌሚንግ እና ሞርሄድ (1998)፣ የተፈጥሮ ጥበቃ (1997)።
የዚህን የስነምህዳር ማህበረሰብ ቡድን ተጨማሪ ፎቶዎች ለማግኘት እዚህ ጠቅ ያድርጉ ።
 © DCR-DNH, ጋሪ ፒ. ፍሌሚንግ.
© DCR-DNH, ጋሪ ፒ. ፍሌሚንግ.
የውክልና ማህበረሰብ ዓይነቶች፡-
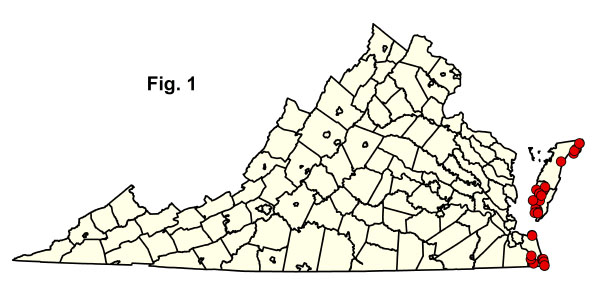
መረጃ የተሰበሰበው በሶስት የውጪ የባህር ዳርቻ ሜዳ አውራጃዎች ውስጥ ከሚገኙ 33 የባህር ረግረጋማ ቦታዎች ነው (ምስል 1)። አብዛኛዎቹ እነዚህ ናሙናዎች በደን የተሸፈኑ ረግረጋማዎች ናቸው, እና ከቁጥቋጦ ረግረጋማዎች ተጨማሪ መረጃ ያስፈልጋል. የቨርጂኒያ የባህር ላይ እፅዋት መረጃ ትንተና በተወሰነ መልኩ የተገደበ ቢሆንም የቨርጂኒያ ዓይነቶችን ስብጥር እና ከUSNVC ጋር ያላቸውን ግንኙነት ለመግለጽ በቂ ይመስላል። ከቼሳፒክ ቤይ ምዕራባዊ የባህር ዳርቻ በዚህ ቡድን ውስጥ ያሉ ማህበረሰቦችን ማስመዝገብ ቅድሚያ የሚሰጠው ጉዳይ ነው። በ NatureServe Explorer የቀረበውን አለምአቀፍ የUSNVC መግለጫ ለማየት ከታች ማንኛውም የደመቀ CEGL ኮድ ላይ ጠቅ ያድርጉ።
 ከዚህ በታች ለተዘረዘሩት ለእያንዳንዱ የማህበረሰብ ዓይነቶች የተቀናበረ ማጠቃለያ ስታቲስቲክስ የተመን ሉህ ያውርዱ ።
ከዚህ በታች ለተዘረዘሩት ለእያንዳንዱ የማህበረሰብ ዓይነቶች የተቀናበረ ማጠቃለያ ስታቲስቲክስ የተመን ሉህ ያውርዱ ።