 የጥበቃ እና መዝናኛ መምሪያ
የጥበቃ እና መዝናኛ መምሪያ መጠበቅ. መከላከል. መደሰት.
 የጥበቃ እና መዝናኛ መምሪያ
የጥበቃ እና መዝናኛ መምሪያ  ማውጫ
ማውጫሞንታኔ ቅልቅል ኦክ እና ኦክ - የሂኮሪ ደኖች
ይህ ቡድን በአንፃራዊነት የተለያየ፣ የተቀላቀሉ የኦክ እና የኦክ-ሂኮሪ ደኖችን ይዟል ከስር በታች ያሉ የተራራማ ቁልቁለቶች እና ቋጥኞች በአብዛኛው በ 600 ሜትር (2 ፣ 000 ጫማ) እና 1 ፣ 200 m (4 ፣ 000 ጫማ) ከፍታ መካከል ይገኛሉ።
Montane mixed oak forests cover extensive areas in western Virginia and generally occupy intermediate positions along major environmental gradients such as soil moisture, soil fertility, and elevation. Soils occupied by montane mixed oak forests are typically less fertile than those of the true montane oak-hickory forests. Overstory composition contains mixtures of chestnut oak (Quercus montana), northern red oak (Quercus rubra), and white oak (Quercus alba). Overstory associates vary with geography and site conditions, but often include sweet birch (Betula lenta var. lenta), magnolias (Magnolia acuminata and Magnolia fraseri), sourwood (Oxydendrum arboreum), hickories (Carya spp.), red maple (Acer rubrum), tulip-tree (Liriodendron tulipifera), and white pine (Pinus strobus). The understories of mixed oak communities usually contain a substantial component of heaths, but also contain many non-ericaceous species such as witch hazel (Hamamelis virginiana var. virginiana), striped maple (Acer pensylvanicum), maple-leaved viburnum (Viburnum acerifolium), mountain holly (Ilex montana), buffalo-nut (Pyrularia pubera), and hazelnuts (Corylus cornuta var. cornuta and Corylus americana). The herbaceous component is relatively diverse, but often patchy and composed of both acidophiles and species characteristic of moderately fertile soils, including New York fern (Parathelypteris noveboracensis), galax (Galax urceolata), Curtis' goldenrod (Solidago curtisii), white wood aster (Eurybia divaricata), indian cucumber-root (Medeola virginiana), squawroot (Conopholis americana), halberd-leaved yellow violet (Viola hastata), speckled wood lily (Clintonia umbellulata), devil's-bit (Chamaelirium luteum), mountain golden-alexanders (Zizia trifoliata), and American lily-of-the-valley (Convallaria pseudomajalis).

Montane oak-hickory forests reach maximal importance on base-rich igneous, metamorphic, and subcalcareous sedimentary rocks. Two types occur throughout western Virginia: a submesic to mesic, rich type with a notably lush herb layer, and a drier, more acidic type with a diverse, often graminoid-dominated herb layer. Northern red oak, white oak, red hickory (Carya ovalis), and shagbark hickory (Carya ovata) are typical co-dominant trees, although in most stands oaks attain greater importance in the overstory than do hickories (Carya spp.), which often reach maximal density and cover in the understory. The chestnut oak is important only in the drier type, while mesophytic trees such as basswood (Tilia americana var. americana and var. heterophylla), bitternut hickory (Carya cordiformis), and sugar maple (Acer saccharum) are frequent associates in the rich type. The shrub layer of these communities is often sparse, and herbaceous composition varies with geography and site conditions. A widespread compositional variant on moist sites features extensive, nearly monospecific colonies of interrupted fern (Osmunda claytoniana). Fertile sites often support a diverse herbaceous flora, including such nutrient-demanding forbs as purple giant hyssop (Agastache scrophulariifolia), white bergamot (Monarda clinopodia), cutleaf coneflower (Rudbeckia laciniata var. laciniata), pale-leaved sunflower (Helianthus strumosus), richweed (Collinsonia canadensis), yellow jewelweed (Impatiens pallida), common black cohosh (Actaea racemosa), starry campion (Silene stellata), stout goldenrod (Solidago squarrosa), hairy-jointed meadow parsnip (Thaspium barbinode), and Appalachian meadow-rue (Thalictrum coriaceum). The luxuriance of such herb layers rivals that of the Rich Cove and Slope Forests. The drier type of montane oak-hickory forest features patch-dominance by Pennsylvania sedge (Carex pensylvanica), Porter's reedgrass (Calamagrostis porteri), wavy hairgrass (Avenella flexuosa), and xerophytic forbs.
የዚህ ቡድን ማህበረሰቦች ወደ ሰሜናዊ ቀይ ኦክ ደኖች በከፍታ ቦታዎች ላይ እና በድሃ ቦታዎች ላይ እና ወደ ሌሎች በርካታ የኦክ እና የኦክ-ሂኮሪ ደኖች በዝቅተኛ የከፍታ ወሰን ይሸጋገራሉ። ከሁለቱም ከመሠረታዊ የኦክ-ሂኮሪ ደኖች እና ከአሲድ ኦክ-ሂኮሪ ደኖች የሚለዩት ከፍ ያለ ከፍታ ባላቸው ቦታዎች ላይ በመገደባቸው በአጠቃላይ > 600 ሜትር (2 ፣ 000 ጫማ) እና ብዙ ታዋቂ ዝቅተኛ ከፍታ ያላቸው ዝርያዎች (ለምሳሌ ምስራቃዊ ሬድቡድ [ሰርሲስ ካናደንሲስ ቫር. ካናዳደንስ] ኮርስ ፍሎሪንግዉዉድ) [Corcis canadensis var. floweringwood]] የሉትም። ከኦክ/ሄዝ ደኖች የሚለዩት እጅግ በጣም ብዙ በሆነ የበታች እና ቅጠላማ ተክሎች ነው። ብዙ የሞንታኔ ቅይጥ ኦክ እና ኦክ-ሂኮሪ ቆሞዎች በ ኛው ክፍለ ዘመን መጀመሪያ ላይ የዚህ ዝርያ የጎለመሱ ግለሰቦች በደረት ኖት ብላይት ( Cryphonectria parasitica ) ከመጥፋታቸው በፊት በቀድሞው የአሜሪካ ደረት ነት (Castanea dentata ) የበላይነት የነበረው ወይም በጋራ የሚተዳደሩ እፅዋትን 20ይወክላሉ። Hickories (Carya spp.) የአሜሪካን ደረትን ከትርፍ ታሪክ ውስጥ በማስወገድ ትልቅ ጥቅም እንደነበራቸው ይታሰባል፣ እና በዘመናቸው ባሉ የኦክ-ሂኮሪ ደኖች ውስጥ ያላቸው ፅናት እና ቀጣይ ምልመላ ከቅርብ አሥርተ ዓመታት ውስጥ የእሳት መገለልን የሚያንፀባርቅ ሊሆን ይችላል።
ማጣቀሻዎች፡ አዳምስ እና እስጢፋኖስ (1983)፣ ኮሊሊንግ እና ራዊንስኪ (1999)፣ ፍሌሚንግ (2007)፣ ፍሌሚንግ እና ኮሊንግ (2001)፣ ፍሌሚንግ እና ሙርሄድ (2000)፣ ጆንሰን እና ዋሬ (1982)፣ ማክኮርሚክ እና ፕላት (1980)፣ ራዊንስኪ እና ሌሎች ። (1994), Rawinski et al . (1996)፣ ስቴፈንሰን (1982ሀ)፣ ስቴፈንሰን (1982ለ)፣ ስቴፈንሰን እና አዳምስ (1991)።የዚህን የስነምህዳር ማህበረሰብ ቡድን ተጨማሪ ፎቶዎች ለማግኘት እዚህ ጠቅ ያድርጉ ።
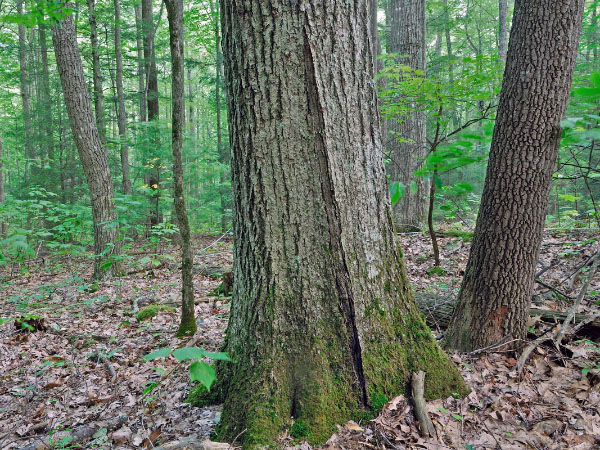 © DCR-DNH, ጋሪ ፒ. ፍሌሚንግ.
© DCR-DNH, ጋሪ ፒ. ፍሌሚንግ.
ይህ ቡድን በምእራብ ቨርጂኒያ ከሚገኙት አብዛኞቹ አውራጃዎች እና ጥቂት ወጣ ያሉ የፒዬድሞንት ጣቢያዎች በ 244 ሴራ ናሙናዎች ተወክሏል (ምስል 1)። የስድስት የማህበረሰብ ዓይነቶች ምደባ በብዙ ትላልቅ ክልላዊ ትንተናዎች የተደገፈ ነው። ሆኖም የቡድኑ የደቡብ አፓላቺያን ተወካዮች በግዛት ውስጥ ያላቸውን ሙሉ ስርጭት ለመወሰን ተጨማሪ ክምችት ያስፈልጋቸዋል። በ NatureServe Explorer የቀረበውን አለምአቀፍ የUSNVC መግለጫ ለማየት ከታች ባለው ማንኛውም የደመቀ CEGL ኮድ ላይ ጠቅ ያድርጉ። ከዚህ በታች ለተዘረዘሩት ለእያንዳንዱ የማህበረሰብ ዓይነቶች የተቀናበረ ማጠቃለያ ስታቲስቲክስ የተመን ሉህ ያውርዱ 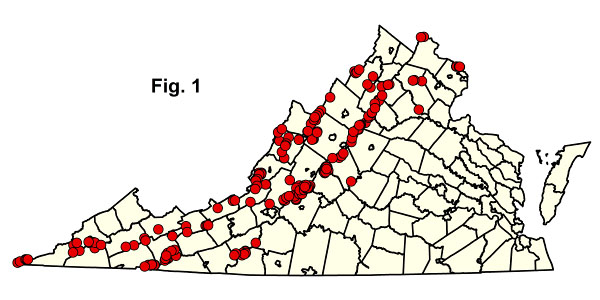
 ።
።