 የጥበቃ እና መዝናኛ መምሪያ
የጥበቃ እና መዝናኛ መምሪያ መጠበቅ. መከላከል. መደሰት.
 የጥበቃ እና መዝናኛ መምሪያ
የጥበቃ እና መዝናኛ መምሪያ  ማውጫ
ማውጫየበለጸጉ ኮቭ ደኖች
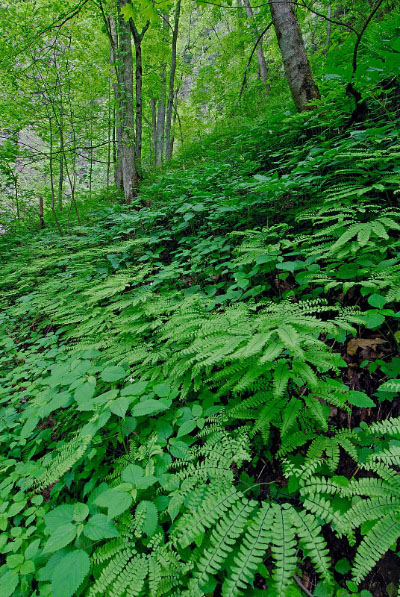
The mixed hardwood forests of this group occupy fertile, mesic, mountain-slope habitats at elevations ranging from about 300 m (1,000 ft) commonly to 1,100 m (3,600 ft), and occasionally higher. Distributed locally throughout western Virginia, these forests are strongly associated with moist, sheltered, landforms (i.e., coves, ravines, and concave lower slopes). Soils may be weathered from various substrates but are generally moderately acidic to moderately alkaline, with high base saturation. In these habitats, soil fertility appears to be strongly correlated with high base cation levels (particularly calcium, magnesium, and manganese) rather than with high pH, and higher-elevation sites often have soils with surprisingly low pH. Characteristic trees include sugar maple (Acer saccharum), basswoods (Tilia americana var. americana and var. heterophylla), white ash (Fraxinus americana), tulip-tree (Liriodendron tulipifera), bitternut hickory (Carya cordiformis) and yellow buckeye (Aesculus flava); chiefly south of the James River). Herbaceous growth is lush with spring ephemerals and leafy, shade-tolerant forbs such as blue cohosh (Caulophyllum thalictroides), yellow jewelweed (Impatiens pallida), large-flowered trillium (Trillium grandiflorum), wood-nettle (Laportea canadensis), common black cohosh (Actaea racemosa), sweet cicely (Osmorhiza claytonii), Virginia waterleaf (Hydrophyllum virginianum), large-leaf waterleaf (Hydrophyllum macrophyllum), large-flowered bellwort (Uvularia grandiflora), red trillium (Trillium erectum), yellow violets (Viola pubescens and Viola eriocarpa), white baneberry (Actaea pachypoda), two-leaved miterwort (Mitella diphylla), goat's-beard (Aruncus dioicus var. dioicus,), yellow mandarin (Prosartes lanuginosa), showy skullcap (Scutellaria serrata), eastern blue-eyed-mary (Collinsia verna), Guyandotte beauty (Synandra hispidula), glade fern (Homalosorus pycnocarpos), and many others. Compositional variation related to substrate and elevation is complex but the group partitions convincingly into several major community types. The principal threats to rich cove forests are logging and invasion by shade-tolerant, non-native weeds, especially garlic-mustard (Alliaria petiolata). The frequent to common white ash component of these communities is undergoing widespread mortality from Emerald Ash Borer outbreaks.
የበለጸገ ኮቭ እና ተዳፋት ደኖች ከተመሳሳይ የመሠረታዊ የሜሲክ ደኖች የሚለዩት በተገደበ የሞንታኔ ስርጭት; በከፍታ ቦታዎች ላይ መከሰት; እና በዋነኛነት አፓላቺያን፣ ከፍተኛ ከፍታ ያላቸው ዝርያዎችን የሚያሳዩ የአበባ ቅንብር።
ማጣቀሻዎች፡ Coulling እና Rawinski (1999)፣ ፍሌሚንግ (1999)፣ ፍሌሚንግ እና ኮሊንግ (2001)፣ ፍሌሚንግ እና ሙርሄድ (1996)፣ ፍሌሚንግ እና ሙርሄድ (2000)፣ ጆንሰን እና ዋሬ (1982)፣ ኦልሰን እና ሁፕ (1986)፣ ራዊንስኪ እና ሌሎችም። (1994)፣ Rawinski et al. (1996)፣ ራይንሃርት እና ዋሬ (1984)።
የዚህን የስነምህዳር ማህበረሰብ ቡድን ተጨማሪ ፎቶዎች ለማግኘት እዚህ ጠቅ ያድርጉ ።

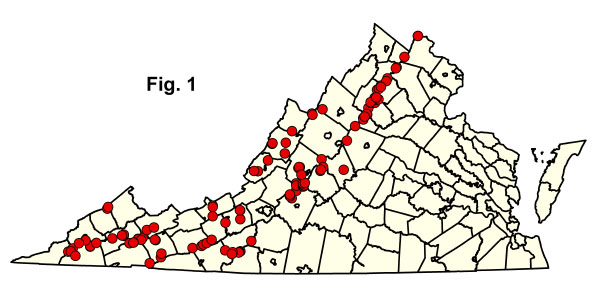
የዚህ ቡድን ምደባ በ 34 የቨርጂኒያ አውራጃዎች (ምስል 1) ውስጥ በተነሱት 119 ቦታዎች ላይ በመተንተን ላይ የተመሰረተ ነው። አብዛኛዎቹ ቦታዎች ለብሔራዊ ፓርክ አገልግሎት በተለያዩ የመድበለ-ግዛት፣ ክልላዊ ምደባ ጥረቶች (ለምሳሌ፣ ብሔራዊ ካፒታል ክልል እና የአፓላቺያን መሄጃ እፅዋት ካርታ ስራ ፕሮጀክቶች) ተተንትነዋል። የአራቱን የተከፋፈሉ ዓይነቶች ሙሉ የግዛት ጂኦግራፊያዊ ክልሎችን ለመወሰን አንዳንድ ተጨማሪ መረጃ መሰብሰብ ያስፈልጋል። በ NatureServe Explorer የቀረበውን አለምአቀፍ የUSNVC መግለጫ ለማየት ከታች ማንኛውም የደመቀ CEGL ኮድ ላይ ጠቅ ያድርጉ።
 ከዚህ በታች ለተዘረዘሩት ለእያንዳንዱ የማህበረሰብ ዓይነቶች የተቀናበረ ማጠቃለያ ስታቲስቲክስ የተመን ሉህ ያውርዱ ።
ከዚህ በታች ለተዘረዘሩት ለእያንዳንዱ የማህበረሰብ ዓይነቶች የተቀናበረ ማጠቃለያ ስታቲስቲክስ የተመን ሉህ ያውርዱ ።